Private cloud services is a virtualized hosting environment that employs computer, network, and storage resources to support application and data processing without sharing them with another organization. On an on-site server, within a virtual machine, or on a remotely managed single-tenant server, a private cloud services can be built. Learn more on uley.info
Contents
Private Cloud Services: What is it?
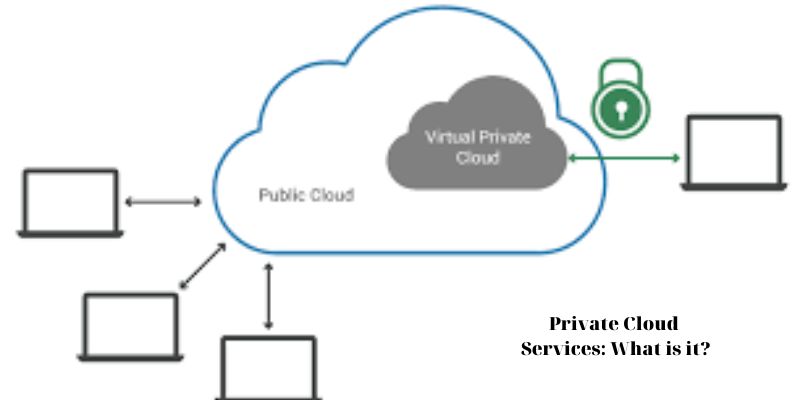
An organization with just one user gets exclusive access to the infrastructure in a private cloud, a sort of cloud computing. An organization’s data center, a third-party colocation facility, or a private cloud provider who provides private cloud services hosting services and may or may not also supply typical public shared multi-tenant cloud architecture are all options for hosting a private cloud.
As with a standard on-premises infrastructure, the end-user company is often in charge of running a private cloud services, which involves continuous upkeep, upgrades, OS patches, middleware, and application software administration.
Though it necessitates a far higher degree of IT experience than using a public cloud, private cloud services solutions give enterprises more control over and better security of private cloud services servers.
Use Private Cloud Services For What Purposes?
As with conventional on-premises infrastructure, private cloud services provide the same level of protection and control. Here are some explanations for why businesses choose private cloud computing:
Security: Since a private cloud services often only receives the organization’s own transactions, private cloud security is improved. Public cloud providers have to manage traffic from millions of users and transactions at once, increasing the possibility of fraudulent activity. Private clouds have their own physical infrastructure, which gives the company more control over the server, network, and application security.
Performance that can be predicted: Workload performance can be predicted since the hardware is dedicated rather than multi-tenant, and it is unaffected by other businesses sharing infrastructure or bandwidth.
Savings over the long run: While setting up the infrastructure to support a private cloud services might be costly, it can be worthwhile. A private cloud can be significantly less expensive in the long run than paying monthly fees to utilize someone else’s servers on the public cloud if an organization already possesses the gear and network needed for hosting.
Cost predictability: Depending on consumption, storage prices, and data egress fees, public cloud expenses might vary greatly. No matter what workloads a business runs or how much data is transported, private cloud services charges remain constant month to month.
Regulatory governance: Locations for computation and storage of data may be governed by laws like the EU’s GDPR. It can be necessary to use a private cloud in those areas where public cloud providers are unable to provide service. In order to guarantee that they have total control over personally identifiable or sensitive information, enterprises with sensitive data, such as financial or legal firms, may choose private cloud storage.
What distinguishes the Private Cloud Services from the Public Cloud?
In a private cloud, the system is hosted and managed by a single company, and the computing resources are devoted and proprietary. The hardware layer underneath is isolated from the infrastructure of any other client, making it private. Services in a public cloud are owned and managed by a provider who also hosts other tenants. In a hybrid or multi-cloud system, businesses can mix a private cloud with a public cloud.
It is possible for an organization to organize workloads between the two environments with the help of a hybrid cloud, which integrates private and public cloud infrastructure. According to this paradigm, the private cloud and public cloud combine to create a single, unified cloud. The underlying software and services utilized by both the public and private clouds must be highly compatible in order to implement a hybrid cloud deployment.
Due to its ability to transfer workloads between private and public clouds when computing requirements and costs change, this approach can give a firm better flexibility than either a private or public cloud.
Businesses that deal with massive data processing as well as those with highly dynamic workloads should consider a hybrid cloud. For maximum efficiency in each case, the company can divide the workloads across the clouds, assigning host-sensitive activities to the private cloud and more taxing, less specialized distributed computing duties to the public cloud.
The hybrid cloud approach gives up some of the entire control of the private cloud and some of the simplicity and convenience of the public cloud in exchange for its flexibility.
Why choose VMware for your Private Cloud Services platform?
A solution provided by VMware Private Cloud, a market leader in cloud infrastructure, allows businesses to easily combine all of their servers into a single resource that can then be shared across virtual machines (VMs) that execute application workloads across the enterprise.
The three main types of private clouds are supported by VMware: managed, hosted, and virtual private clouds.
The Benefits Of Private Cloud Services

The fact that customers of a private cloud do not share resources is its fundamental benefit. A private cloud computing architecture is appropriate for enterprises with dynamic or unexpected computing demands that demand direct control over their environments due to its proprietary nature, often to fulfill security, corporate governance, or regulatory compliance requirements.
Most of the advantages of public clouds, including user self-service, scalability, and the capacity to create and configure virtual machines (VMs) as well as adjust or optimize computing resources on demand, may be provided by a private cloud when it is designed and implemented appropriately by an enterprise. A company can also use chargeback or showback solutions to monitor computer consumption and make sure that business units only pay for the resources or services they really utilize.
Conclusion
It might be challenging to comprehend price structures for managed private cloud deployments. There isn’t usually a straightforward private cloud bundle available on vendor websites. They instead provide a variety of gear, software, and services that a business may employ to set up a private cloud. On vendor websites, these goods’ prices are frequently not made apparent, and customers are encouraged to interact with a salesperson once they have arrived at the page that concentrates on purchase intent.


